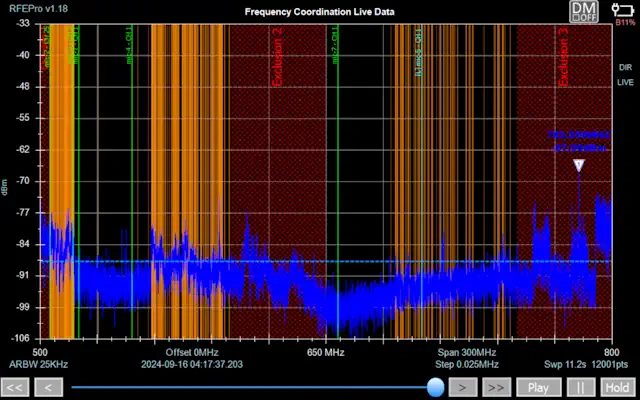
RF Explorer Pro Frequency Coordination
Overview
The RF Explorer Pro serves as a powerful tool to understanding and implementing effective RF frequency coordination strategies and is useful whether you are a seasoned RF engineer, a communication network operator, audio engineer or someone new to the field.
Required License RFEPLIC52 - Frequency Coordination
For more details visit link below:
Configuration Options
Freq Coord Display
Threshold
Show or hide the threshold value in both the Analysis and Realtime graphs.
IMD 3 Order
Show or hide third-order intermodulation products on the Analysis graph.
IMD 5 Order
Show or hide fifth-order intermodulation products on the Analysis graph.
Noise Bands
Show or hide the frequency ranges identified as noise bands on the Analysis graph.
Exclusions
Show or hide defined frequency exclusion ranges on the graph.
Threshold Color
Select the color used to display the threshold line on the graph.
Sweep Exclusions
When unchecked, exclusion ranges are removed directly from the analyzer sweep, significantly improving sweep efficiency and responsiveness.
Notes
- Intermodulation products and noise bands are not displayed in the realtime Frequency Coordination graph to avoid excessive visual clutter.
- You can experience significantly faster analyzer sweeps by disabling the “Sweep Exclusions” option (up to 2x to 5x faster). This optimization not only increases performance but also provides a smoother and more responsive experience, especially when working with complex exclusion setups.